Polymers extracted from the ground can make cement more climate-friendly

Concrete is everywhere around you – in the foundation of your house, the bridges you drive over, sidewalks and city buildings. that it It is often described as the The second most widely used substance By volume on land after water.
But the way concrete is manufactured today also makes it a major contributor to climate change.
Portland cement, the main component of concrete, is responsible for approx 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions. This is because it is made by heating limestone to high temperatures, a process that burns a large amount of fossil fuels for energy and releases carbon dioxide from the limestone in the process.
The good news is that there are alternatives, and they are gaining attention.
Portland cement: the greenhouse gas problem
Cement-like materials have been used in construction for thousands of years. Architects have found evidence of their use in… Pyramids of Egypt Buildings and water canals Roman Empire.
Portland cement commonly used in construction today was patented in 1824 by Joseph Aspdin, British builder.
The preparation of modern cement begins with crushing raw materials extracted from limestone and clay and then heating them In an oven in About 2650 degrees Fahrenheit (about 1450 °C) to form ClinkerSolid, rock-like remains. The clinker is then cooled and ground with gypsum into a fine powder called cement.
About 40% of carbon dioxide emissions come from cement production It comes from burning fossil fuels To generate the high heat necessary to operate the furnace. The rest comes as heat It converts limestone (calcium carbonate) into lime (calcium oxide), and releases carbon dioxide.
In everything, between Half ton and 1 ton Greenhouse gases are released per ton of Portland cement. Cement is a binding agent that, mixed with water, holds aggregate together to form concrete. It’s a pose About 10% to 15% Of concrete mix by weight.
Alternative technologies can reduce emissions
With the increase in population and cities and the need for new infrastructure, The use of cement is increasingThis makes it important to find alternatives with lower environmental costs.
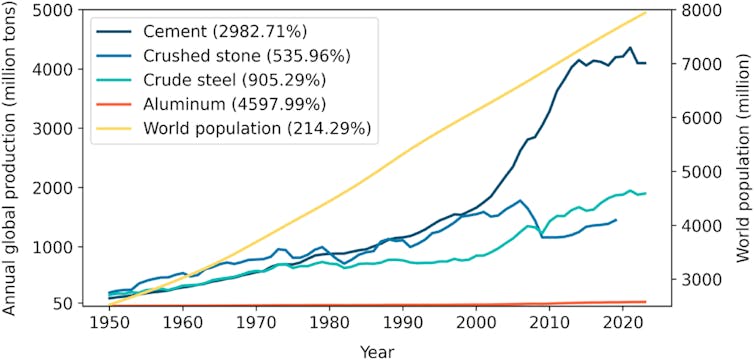
Hao Chen et al., 2025, CC BY-NC-ND
Some techniques to reduce carbon dioxide emissions include replacing some of the clinker – the solid residue usually made of limestone – with clinker. Supplementary materials Such as clay, fly ash and slag resulting from industries. Other methods reduce the amount of cement by: Mix in waste sawdust Or recycled Materials such as plastic.
But the long-term solution to reducing cement emissions is to completely replace conventional cement with alternatives. One option is Geopolymers Made from earthen clay and industrial waste.
Geopolymers: a more climate-friendly solution
Geopolymers can be made by mixing clay-like materials rich in aluminum and silicon minerals with a chemical activator through a process called Geological polymerization. The activator converts silicon and aluminum into a cement-like structure. All of this can happen at room temperature.
The main difference between cement and geopolymer is that cement is mainly composed of calcium, while geopolymers are made of silicon and aluminum with some possible calcium in their structure.
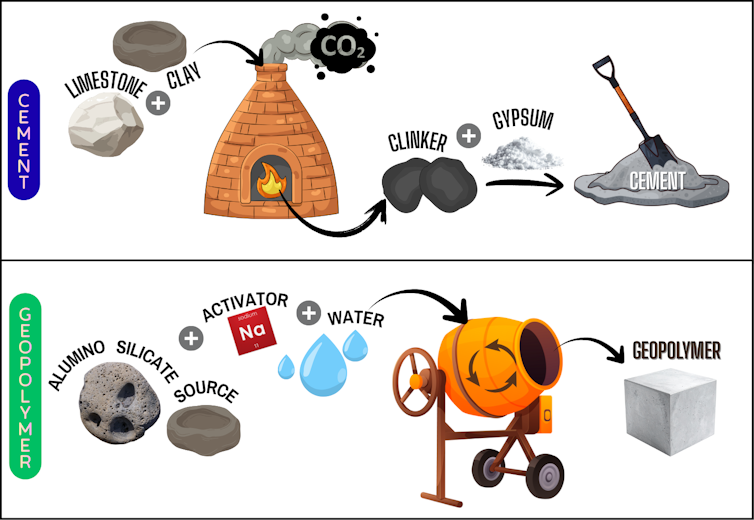
Alsina Johnson Sudagar, CC BY-NC
It has been found that these geopolymers possess High strength and durabilityincluding flexibility in Freezing and thawing cycles And resistance to Heat and fireThese are important requirements in construction. Studies have found that some geopolymers can provide it Similar if not better strength than traditional cement Because it does not require heat as clinker does, it can be produced using it Significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions.
Geopolymers can also be produced from a variety of raw materials rich in aluminum and silicon, including earth materials. clay, Fly ash, Blast furnace slag, Rice husk ash, Iron ore waste and Recycling of construction brick waste. Geopolymer technology can be adapted depending on the clay or industrial waste locally available in the area.
An additional advantage of geopolymers is that changes in the mixture can produce a range of features.
For example, Me and my fellow researchers At the University of Aveiro in Portugal, they added a small amount of cork industry waste — leftover from making bottle stoppers — to geopolymer clay, and found that it could… Improve the strength of the material by up to two-fold. Cork molecules filled the voids in the geopolymer structure, making it denser, which increased its strength.
Likewise, additives such as Sisal fiber from the aloe vera plant, Recycled plastic and Steel fibres It can change the properties of the geopolymer. Additives are not involved in the geopolymerization process but act as fillers in the structure.
Geopolymer structures can also be designed to act as absorbents, Attraction of toxic metals in wastewater and – Capturing and storing radioactive waste. Specifically, merge Materials such as zeolite Which are natural absorbents in the geopolymer structure can make them useful for such applications as well.
Where geopolymers are now used
Geopolymers have been used in… Many types of constructionincluding roads, coatings, 3D printing, coastal environmental protection, steel and chemical industries, sewer rehabilitation, radiation protection building, missile launch pad and bunker infrastructure.
One of the earliest examples of a modern geopolymer concrete project was the Brisbane West Wellcamp Airport in Australia.
It was built in 2014 with 70 thousand metric tons of geopolymer concreteIt is estimated that it reduced carbon dioxide emissions resulting from the project by a percentage As much as 80%.
The geopolymer market is currently estimated to be between 7 billion US dollars and 10 billion dollarswith The largest growth is in the Asia-Pacific region.
Analysts estimate that the market could grow at a rate 10% to 20% annually It reaches approx $62 billion by 2033.
In several countries, Greenhouse gas regulations and green building certifications It is expected to support the continued growth of geopolymers in the construction industry.
Expanding the use of cement alternatives
However, the advantage of using industrial waste in geopolymers is a double-edged sword. The composition of industrial waste varies, so standardization of treatment methods may be difficult. Geopolymer components must be mixed in certain proportions to achieve the desired properties.
Geopolymer doping production, typically performed in chemical facilities, can drive up the cost and contribute to the carbon footprint. Long-term data on the stability of these materials has only now been developed due to their novelty. These geopolymers can also… It takes longer to adjust of cement, although the setting time can be accelerated by using raw materials that react quickly.
Development of cheaper and naturally available steroids e.g Rice husk from agricultural waste With sustainable supply chains it can help reduce costs and environmental impact. Printing the recipe on the raw material packaging can also help simplify the task of determining the mixing ratio so that geopolymers can be used more widely with confidence.
Although geopolymer technology has some drawbacks, these low-carbon alternatives have great potential to reduce emissions from the construction sector.



